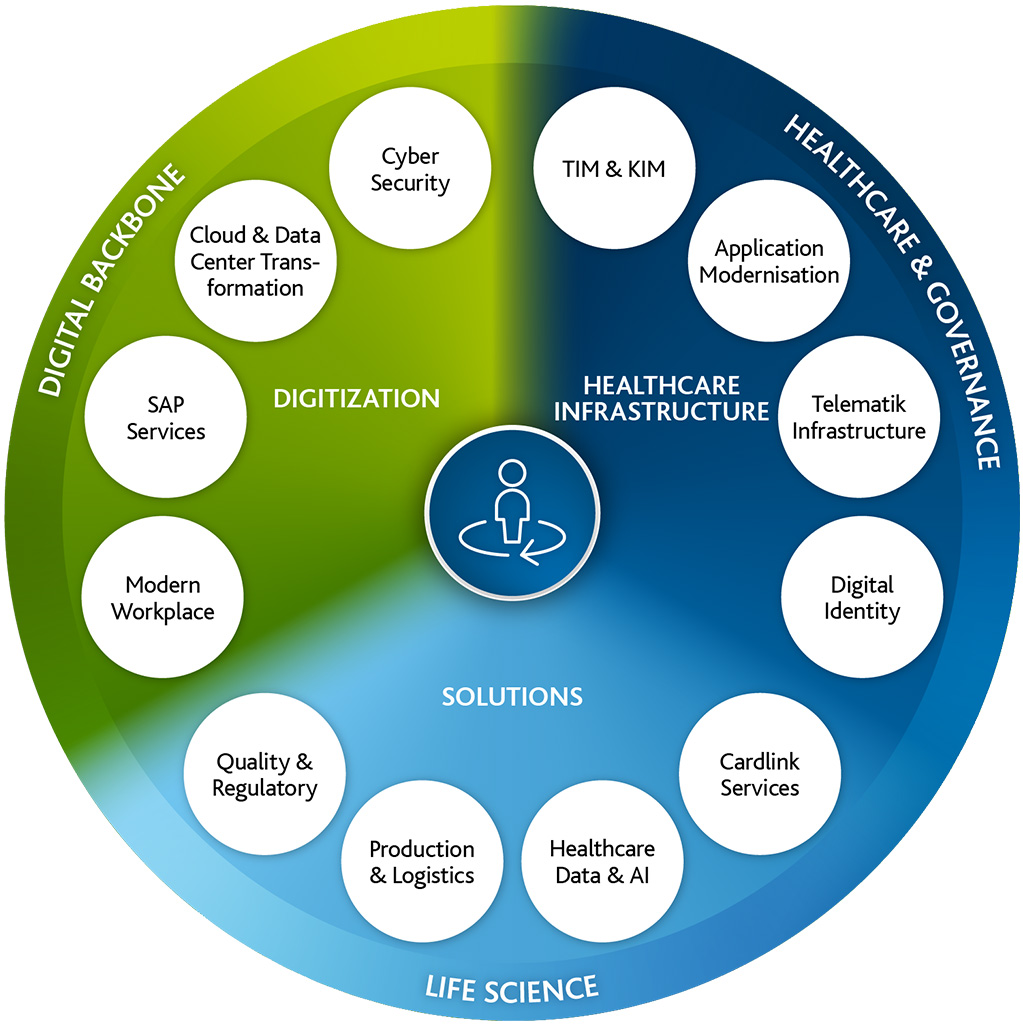
Digitization Partner for the Healthcare and Life Science Industry
Future-Proof: Our Digital Solutions for Healthcare and Life Science
We’re Improving Healthcare. Digital.
Because with our solutions, we pursue the goal of making the healthcare industry more future-proof and optimizing business processes in the life science industry. As thought leaders, we support companies in the healthcare sector in withstanding cost pressure and optimally exploiting the advantages of digitization. We meet our customers at eye level and accompany them in partnership with their cloud and outsourcing strategy.


With NAVOO®, we have achieved our goal of ensuring efficient and secure global collaboration for B. Braun employees with just one innovative solution. The satisfaction of our employees in their daily teamwork speaks for the success of the project.
Worth Knowing
-
What is the gematik telematics infrastructure?
gematik's telematics infrastructure (TI) is a secure, Germany-wide platform in the healthcare sector that allows digital applications and medical data to be exchanged between different service providers such as doctors and all other employees in the sector. The TI is part of the digitization strategy in the healthcare sector and is intended to improve the quality of medical care and increase efficiency and patient safety. The TI's central services have been operated by Arvato Systems since 2015.
The consistent further development of the telematics infrastructure based on a zero-trust infrastructure (TI 2.0) reduces complexity and ensures a user-friendly, more flexible, dynamic digital healthcare system.
-
What applications are running in the telematics infrastructure?
Here are some examples of applications running in the TI:
Electronic Health Record (ePA): the ePA is a digital health record where patients can store their medical data. As an application of the TI, it is designed to facilitate the exchange of health data between different healthcare providers.
Electronic certificate of incapacity for work (eAU): The eAU is a digital certificate of incapacity for work issued by physicians and transmitted to health insurers via the TI.
Electronic Medication Plans (eMP): The eMP is a digital medication plan that contains important information about a patient's medication. The eMP is designed to help prevent medication errors.
Emergency Data Management (NFDM): NFDM is a directory that stores important patient medical information. NFDM enables rapid and targeted medical assistance in an emergency.
E-prescription: The e-prescription is digitally created as well as signed, and issuance is mandatory for all those with statutory health insurance. The prescription code can be redeemed either on the smartphone or by printing it out at a pharmacy. Using the app gives patients secure, privacy-compliant access to prescription data.
Other apps include KIM (Communication in Medicine), TIM (TI Messenger), ISiK, or DEMIS.
-
What is the FMD?
The abbreviation FMD stands for the "Falsified Medicines Directive". The FMD is an EU directive that came into force in February 2019 and aims to protect consumers from falsified medicines.
Under the FMD, all prescription medicines manufactured or imported in the EU must be marked with a unique identifier. The identifier consists of a two-dimensional data matrix code that contains information such as the product name, batch number, and expiration date. The data is stored in a Europe-wide database and can be accessed by manufacturers, wholesalers, pharmacies, and monitoring authorities. The FMD thus ensures that only genuine and safe medicines are delivered.
-
How does a strategic path to the cloud work?
A modern IT infrastructure is critical to achieving business goals and competitive advantage. Flexibility and adaptability, cost reduction, increased efficiency, cyber security, and data protection are just a few reasons why companies should opt for the cloud.
In order to fully exploit the advantages of modern cloud IT in line with business requirements and at the same time minimize risks, the existing IT landscape must be considered individually, and a custom-fit roadmap must be developed at the application level. Depending on the application and business relevance, there are usually different migration and operating scenarios that need to be implemented according to requirements.
Learn here more about our approach from requirements gathering to technical analysis and solution design.
-
What is the Sovereign Cloud?
The aim of a sovereign cloud is to reduce dependence on foreign cloud providers and retain control over one's data. It should be ensured that technical measures exclude direct access from outside. The government or a selected organization can carry out the operation. This is particularly important for government agencies, critical infrastructures, and other organizations with sensitive data. This allows them to use globally established technologies under local sovereignty criteria.
-
How does cyber extortion work in the healthcare and life sciences industry?
Cyber-extortion in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries can occur in a variety of ways. Here are some examples:
Ransomware: Attackers penetrate a healthcare or life sciences company's IT system and encrypt important files or systems. They then demand a ransom to restore the encrypted data.
Data leaks: This involves stealing sensitive data from companies' systems and threatening to make the data public. A ransom is demanded to get the data back.
DDoS attacks: An attacker carries out distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks against systems to affect availability. He or she then demands a ransom to stop the attacks.
Social engineering: Cybercriminals impersonate employees of the healthcare or life sciences company and ask alleged colleagues to transfer sensitive information or money.
Certifications
Rely on us: information security, quality management, IT service management. For our customers, we regularly have our performance measured and extensively certified. You benefit in the long term from our adherence to the highest quality standards and our technological expertise in the form of a trusting and highly professional collaboration.
Your Contact for Healthcare & Life Science





































