AI Basics at a Glance
What's behind AI, ML, DL and LLM
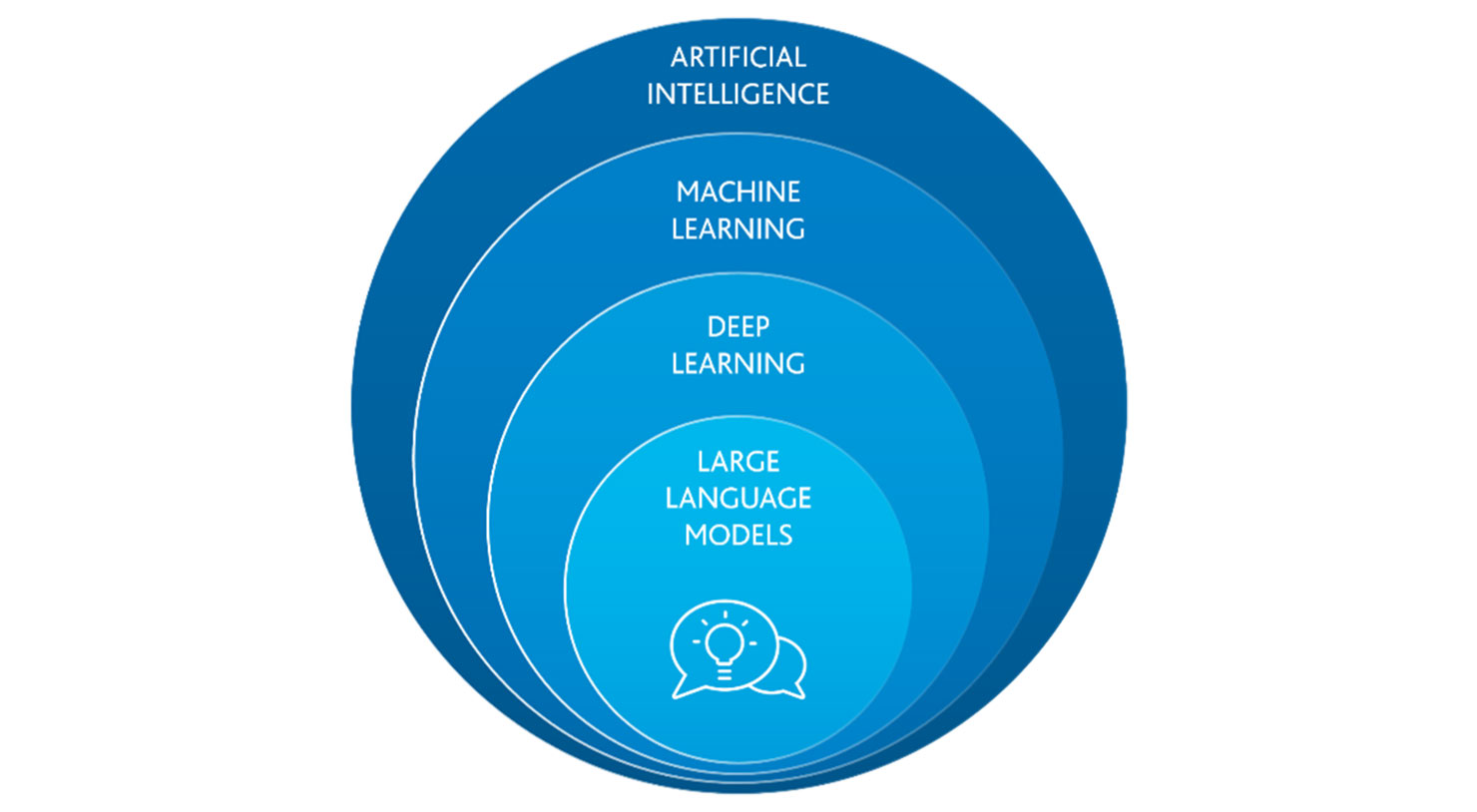
The impressive results achieved by large language models such as ChatGPT have made Artificial Intelligence (AI) experience an enormous upswing. AI is gradually finding its way into many areas of our lives, changing how we work daily. It makes sense to start with a brief classification to better understand the current large language models and their potential applications. This is how Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Large Language Model (LLM) are related.
Artificial Intelligence
The term Artificial Intelligence (refers to an area of computer science that deals with the creation and development of machines or software. These applications are able to perform tasks that normally require human thought. In the context of the digital workplace with Microsoft 365 this includes tasks such as creating presentations, writing emails or answering questions based on specific data.
Machine Learning
Machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, aims to establish a relationship between input and output data. It can solve problems that are too complex to be translated into simple rules but for which a lot of sample data exists. This sample data is used to train a model that can then be applied to new, unknown data. Common examples are the detection of credit card fraud, diagnostic procedures, or text recognition.
Deep Learning

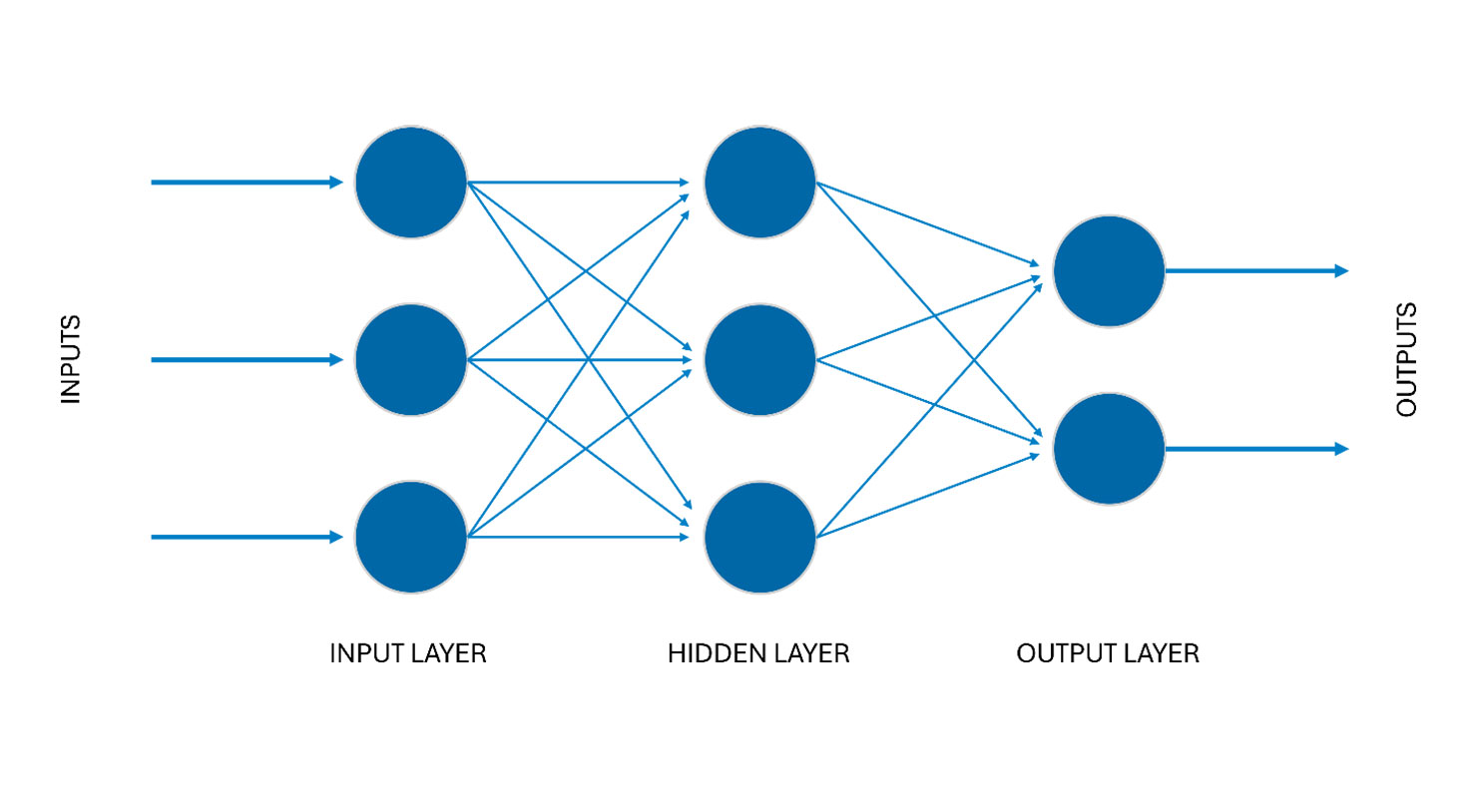
Deep learning takes the idea of machine learning further and transfers it to far more complex use cases. Multi-layered, artificial neural networks are used for this purpose. As with machine learning, these models must first be trained with a lot of data. However, the goal remains the prediction of output values based on inputs.
Large Language Models
Large language models are deep learning models that can understand and generate language. They are trained using enormous computing power with a large amount of data. The aim of a large language model is to predict the next word in an existing chain of words. As with deep learning and machine learning, the aim is to establish a connection between input parameters (a list of words) and the desired output (the next word).
Probably the best-known representative of LLMs is ChatGPT in its various versions.
Generative pre-trained transformer
The GPT in ChatGPT stands for generative pre-trained transformer and describes the three main components of the model:
Generative means that the model is able to generate new texts that are based on or continue a given input text. Based on probabilities, the model determines the next word token to be added to the input text. The result is then run through the model again.
Pre-trained means that the model has been trained in advance with a large amount of text data in order to learn a general language representation. Pre-training enables the model to capture various linguistic patterns and relationships in natural languages, but without performing a specific task.
Transformer refers to the actual architecture of the neural network. A transformer consists of two main components: An encoder, which converts the input text into an abstract representation that captures the meaning and relationship of words, and a decoder, which takes the result of the encoder and generates the output text from it.
Pre-training and instruction training
Although the model acquires a great deal of knowledge through pre-training, it is not able to perform specific tasks. For example, the model still has to learn how to respond to a question with a clear, precise answer. This requires further training, which is called instruction training or instruction fine-tuning. The training data is much smaller here, but contains specific examples of tasks and expected outputs.
Written by

Erik Jungnickel is a software developer with over 15 years of practical experience. His focus is on the front-end development of modern web applications and the use of AI technologies with Microsoft Azure. He designs innovative and future-proof solutions by combining technical depth, cloud know-how, and practical experience.